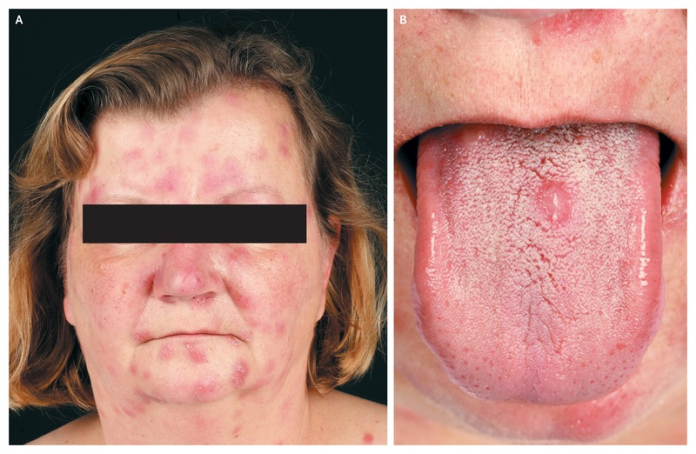
A 54-year-old woman presented with erythematous asymptomatic lesions with a history of 3 weeks. Physical examination revealed lesions on the face, tongue, trunk and lower legs. Initially, the papules and nodules appeared on the face and tongue of the patient. However, the lesions subsequently spread to her lower legs and trunk in the absence of any other systemic symptoms.
After obtaining the medication history of the patient, it was found that the patient had taken oral penicillin G, two weeks earlier, for treatment of sore throat. Although, after a few days she developed an angioedema, after which she stopped taking the antibiotics. Skin lesion biopsy revealed an inflammatory infiltrate with multiple plasma cells, which suggested the diagnosis of secondary syphilis. The diagnosis was confirmed based on a positive assay for T. pallidium IgM and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of value 5770 U per millilitre (normal range 0 to 24) and Treponema pallidium particle agglutination with a titer of 1:160,000 (normal range, 0 to 640).
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of the lesions included cutaneous sarcoidosis and leukemia cutis. The patient received a final diagnosis of papulonodular secondary syphilis with most likely a syphilitic pharyngitis and mucous plaques.
Treatment
The patient was treated with intravenous ceftriaxone for 3 weeks with a daily dose of 2 g because of previous intolerance to penicillin. After initiation of treatment, the rash cleared within 4 weeks.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease and which is caused by bacteria, Treponema palladium, mainly transmitted by sexual contact. In addition, the history of the disease shows that it has evolved with alternating periods of activity distinct histopathological, immunologic and clinical characteristics.
The secondary stage of the bacterial infection is accompanies with polymorphism and polyadenomegaly of cutaneous lesions. Moreover, clinical presentations, among others include corymbiform, psoriasiform, lichenoid, follicular, papular and macular lesions, as in this case. However, the presentation of secondary syphilis with papular and nodular lesions is rare with just 15 cases that have been reported over the past 20 years in literature.
References
Ziegler, B., & Booken, N. (2013). Papulonodular Syphilis. The New England journal of medicine, 368(6), 561-561.