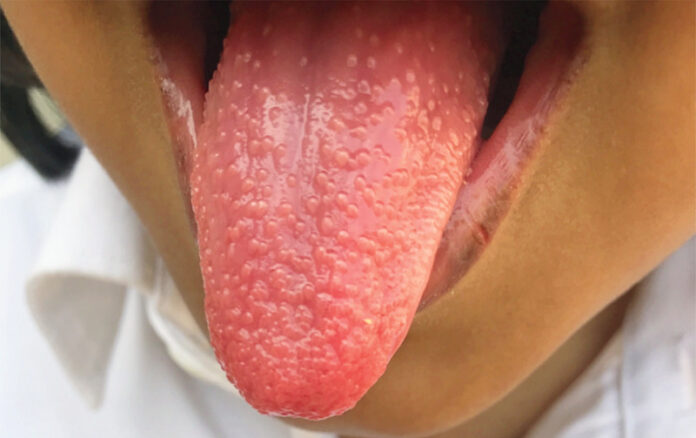
A 5-year-old girl presented with a sore throat, fever, and a strawberry tongue. The paediatrician diagnosed streptococcal pharyngitis
Parents brought their 5-year-old girl to the outpatient department of paediatrics with complaints of fever, sore throat, and odynophagia (pain on swallowing) for the past 3 days. However, the patient did not have any associated cough, runny nose, or hoarseness. The paediatrician observed strawberry tongue on examination.
Physical examination revealed a generally ill girl with a body temperature of 40°C. Moreover, she had dry mucous membranes, fissured lips, a red tongue with enlarged papillae, enlarged and edematous tonsils with exudates. Additionally, she had tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy.
However, the girl had no rash, conjunctival congestion, oral ulcers, or splenomegaly.
Serological investigations revealed a white blood cell count of 14,400 with 73.0% neutrophils, 19.0% lymphocytes. Additionally, it also showed 0.9% atypical lymphocytes.
The throat culture grew group A streptococcus; therefore, the pediatrician confirmed the diagnosis of streptococcal Pharyngitis.
Since the strawberry tongue is a manifestation of other conditions, including Kawasaki disease, allergies, drug-induced, toxic shock syndrome, B12 deficiency, etc.; therefore, it is imperative to take a thorough history, physical examination and perform appropriate investigations to rule out other causes of strawberry tongue.
Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis (GAS), in most patients, is self-limited with symptoms resolving within 5 to 7 days. Moreover, antibiotics reduce the duration and severity of symptoms and prevent the spread of the infection. However, some complications can arise secondary to a GAS infection, which include:
- Acute rheumatic fever (ARF)
- Acute glomerulonephritis
- Scarlet Fever
- Poststreptococcal arthritis (PSRA)
- Streptoccal toxic shock syndrome
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Mastoiditis
- Otitis Media
- Sinusitis
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Streptococcal bacteremia
- Meningitis
The paediatrician treated the girl with oral amoxicillin for 10 days. At the post-treatment follow-up, the patient had recovered completely. Similarly, she had no recurrence of symptoms at the 3- and 6-month follow-up.
References:
Monalisa Sahu, M. B. (2021, March 25). Strawberry Tongue in Streptococcal Pharyngitis. Retrieved from The New England Journal of Medicine: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMicm2026930