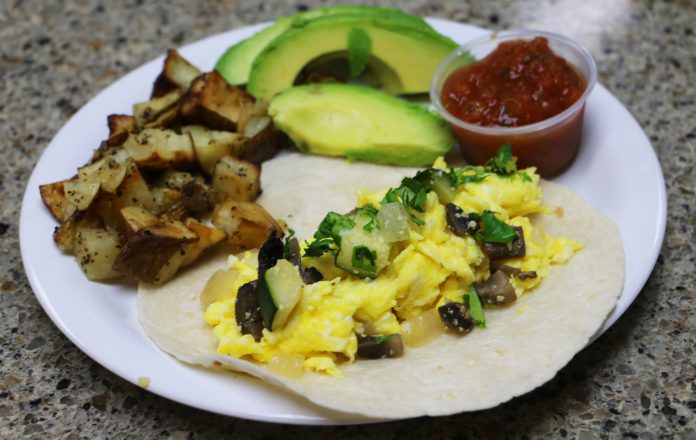
Researchers at the University of Illinois have found evidence that daily consumption of avocados can improve gut health.
Dietary habits involving low fiber and high saturated fat intake result in overweight or obesity. Research has shown that gut bacteria are affected by such dietary habits and thus result in weight gain. In the past scientists have often regarded avocados as a tool for weight loss due to their high fiber content. The high fiber and monosaturated fat content in avocados can influence an individual’s weight by decreasing hunger and reducing blood lipid concentration. However, not much is known about their effect on the gut bacteria.
Therefore, researchers at the University of Illinois set out to discover avocados’ effect on gut health. They aimed to explore the effect of the high fiber and fat content on the gut bacteria and the health outcomes of the changes. They published their findings in the Journal of Nutrition.
We know eating avocados helps you feel full and reduces blood cholesterol concentration, but we did not know how it influences the gut microbes, and the metabolites the microbes produce.
Sharon Thompson, lead author
Daily Consumption of Avocados Improve Gut Health
The researchers hypothesized that daily consumption of avocados would increase the gut bacteria responsible for fiber degradation. Thus, improving gut health.
To test their hypothesis, they recruited 163 overweight or obese adults. The participants were otherwise healthy. Participants then received one meal containing avocados as a meal replacement for either breakfast, lunch, or dinner, daily for a period of 12 weeks. A control group received a similar meal in terms of energy and macronutrient composition, but minus the avocado. Throughout the 12-week study, participants provided blood, urine, and fecal samples. Furthermore, they also provided information about their meal consumption, recording how much they ate.
Rather than weight loss, researchers aimed to investigate the effects of avocado on the gut bacteria.
Verdict? Eat More Fiber.
Results showed that compared to the control group, participants had a greater number of gut bacteria that breaks down fiber. This produced metabolites that lead to improved gut health. Avocado consumption also led to decreased fecal bile acids in the participants. Moreover, despite the avocado group consuming more calories, they had greater fat excretion in their stool.
Greater fat excretion means the research participants were absorbing less energy from the foods that they were eating. This was likely because of reductions in bile acids, which are molecules our digestion system secretes that allow us to absorb fat. We found that the amount of bile acids in stool was lower and the amount of fat in the stool was higher in the avocado group
Hannah Holscher, senior author
Results of the study show the importance of maintaining a healthy gut. Furthermore, the study provides information for nutritionists creating diet plans for overweight or obese adults.
Reference:
Sharon V Thompson et al, Avocado Consumption Alters Gastrointestinal Bacteria Abundance and Microbial Metabolite Concentrations among Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial, The Journal of Nutrition (2020). DOI: 10.1093/jn/nxaa219
Fulgoni VL, Dreher M, Davenport AJ. Avocado consumption is associated with better diet quality and nutrient intake, and lower metabolic syndrome risk in US adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001–2008. Nutr J 2013;12:1.