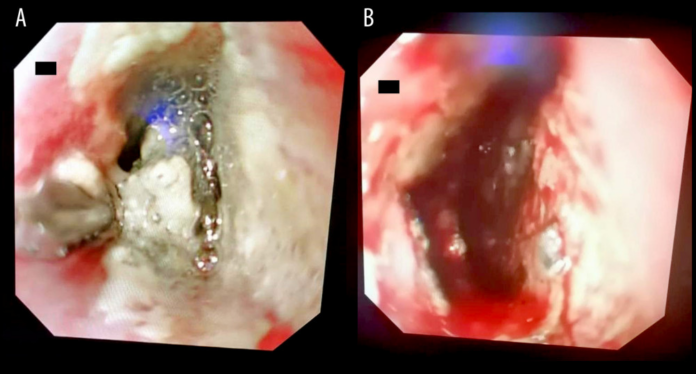
Aortoesophageal fistula after ingestion of a button battery
Cases of infants or children accidentally swallowing button batteries are quite common. This often poses a surgical emergency and may have a fatal outcome. Likewise, in a similar case, a 2-year-old developed an aortoesophageal fistula (AEF), after he swallowed a button battery.
The patient presented with hematemesis, 9 days after ingesting a button battery. Although the battery was successfully removed endoscopically 16 hours after the incident, the patient was aggressively resuscitated. In this rare case, the toddler developed an AEF. An aortoesophageal fistula is a rare, however, fatal disorder that causes gastrointestinal bleeding. In this condition, abnormal communication forms between the oesophagus and aorta. This may be because of a thoracic aortic aneurysm, foreign body ingestion, postoperative complications or esophageal malignancy.
Investigations and diagnosis
The diagnosis is confirmed using computed tomography angiography or using aortography. The patient’s aorta was successfully repaired using a vascular plug device. And was scheduled for a surgical procedure for 2 months later. The aorta repair kept the patient safe for 2 months. Similarly, the defect was surgically repaired using direct anastomosis and was completed with a patch of bovine pericardium, including closure of the fistula using stitches. The AEF was treated successfully using a novel vascular plug device. Whereas aortic endovascular stenting and vascular ocular placement are minimally invasive emergency options that can be used till a definitive treatment is provided. These are lifesaving procedures considered as a bridge for definitive repair. Most commonly used surgical options include aortic repair defect and replacement of the diseased segment with a graft.
In cases of foreign body ingestion, button batteries are most commonly ingested. Complications depend on the age of the child, anatomical abnormalities, duration of retention, site of dislodgement and of course, size of the foreign body. Management of AEF includes aggressive resuscitation, control of bleeding, novel use of a vascular plug device and percutaneous endovascular repair.
Source: American Journal of Case Reports



