- Sublingual epidermoidal cyst is a benign, slow growing and painless sac-like pouch.
- It can be located in the submandibular, sublingual and submental region.
- The cyst can cause symptoms of dysphagia and dyspnea.
- Treatment of choice is surgical excision.
A 73-year-old female patient reported to the emergency department with complaint of difficulty speaking. She further stated that the difficulty she had while speaking had worsened over the course of 4 days. Moreover, according to her medical history, she underwent a dental procedure 2 months earlier. The procedure involved inserting a bridge because of a missing tooth.
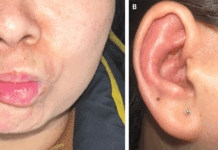
Physical examination of the patient showed a large painless and fluctuant swelling on the anterior floor of the mouth. There was no evidence of palpable cervical lymph nodes or purulent drainage at the orifices of the submandibular and sublingual ducts. For further evaluation, computed tomography of the neck with contrast material was performed, which showed a well-defined midline and suprahyoid cyst that measured 7 cm by 4 cm by 3.5 cm. The cyst was located above the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles.
The lesions also had peripheral enhancement with multiple discrete foci of hypoattenuation that indicated a coalescence of small, fatty nodules. The findings were consistent with the diagnosis of epidermoidal cyst.
Epidermoidal cyst
Epidermoid cysts are benign cysts that are filled with keratin. The cysts are most commonly located on the trunk, neck and face. However, in some cases, can also be present within the floor of the mouth. The cyst of the patient was surgically excised with an intraoral approach. The patient reported a complete resolution of symptoms at follow-up.
References
Thibouw, F., & Schein, A. (2020). A Sublingual Epidermoid Cyst. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(7), 655-655.