The human brain gives knowledge to Artificial Intelligence, enabling it to replicate some of the brain’s functions and learning processes. However, the extent of emulating the activity of the brain is not fully understood.
Researcher Hiroshi Makino recently did a study to identify the possible similarities between the brain and artificial intelligence in solving problems.
He said,
Previous studies in psychology showed that humans and non-human animals combine pre-learned skills to expand their behaviour repertoires
However, how the brain achieves this remains poorly understood. I was inspired by research in deep reinforcement learning (a subfield of AI research) studying the same problem, and empirically tested theoretical predictions derived from it by recording neural activity in the mouse brain.
AI agents take pre-training abilities they have learned and recombine these skills in a hierarchical manner when tackling a new challenge. Makino was interested in investigating the notion that the brain functions similarly.
To accomplish this, he examined how deep reinforcement learning bots picked up new task-solving skills. Then he contrasted this with how mice approached the same novel assignment.
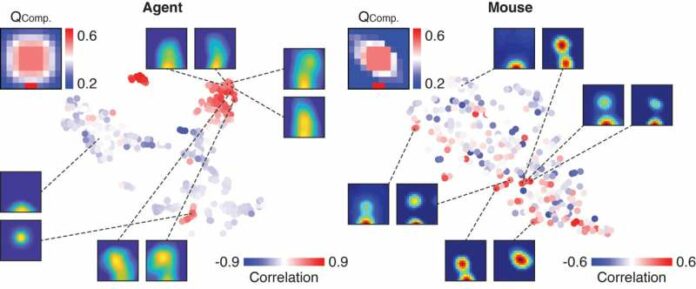
As the mice solved a new problem by combining pre-acquired skills/knowledge, activity was recorded from single neurons in their brains,” Makino explained. “The resulting neural activity was compared with theoretical models derived from deep reinforcement learning where a simple arithmetic operation was used to combine values of pre-learned behaviours.
Similarities between Artificial Intelligence and The Brain
Makino investigated the neural activity of the mouse cortex, as the mice undertook a novel task using previously learned skills. Furthermore, as he approached a new composite problem. He noticed brain representations of action values that mirrored those produced by a deep reinforcement learning algorithm.
He said,
I found similar activity patterns between the artificial agent trained with a deep reinforcement learning algorithm and the brain,
I think one of the major contributions of the study is the integration of neuroscience and deep reinforcement learning to identify a potential mechanism for how the brain composes a new behaviour.
Conclusion
The findings of the study conclude that when a new task is being tackled, the brain consists of a new behaviour. And it is through a simple arithmetic operation on action-value representations with scholastic policies acquired previously.