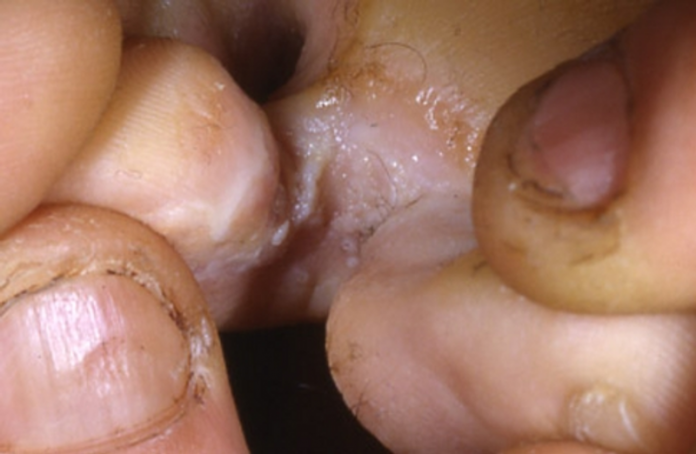
Clinical manifestation of secondary syphilis – macerated plaques of toe webs
Striking outbreaks of syphilis have occurred in recent years in China, Russia, Canada, USA and some areas of Central and Eastern Europe. Syphilis is caused by an anaerobic filamentous spirochete Treponema pallidum. Similarly, it has become more common because of the false sense of security that sexually transmitted diseases are curable, sexual promiscuity and the growing sex industry.
The initial presentation of syphilis is generally in the oral cavity
Secondary syphilis is clinically the least difficult to diagnose. In addition, the clinical manifestations of syphilis, for example, the macular rash can be confused with a variety of skin diseases, in some cases. For example, conjunctivitis, urethritis, reactive arthritis, lichen planus, pityriaisis, drug eruption, psoriasis and eczema can be mimicked by syphilis.
Oral chancres are found in 4 to 12% of patients with primary syphilis and occur at the site of organism penetration into the mucosa. Anatomical sites that are affected commonly include lips, soft palate, gingiva and tongue.

However, the manifestations in secondary syphilis are quite variable. A characteristic feature of the lesions is multiple mucous patches that are slightly raised, surrounded by eryhtema and covered by greyish, white pseudomembranes. Typical sites are vestibular mucosa, tongue, pillars and soft palate.

Secondary syphilis may show unexpected features in some patients
Condyloma lata are white, grey mucous patches that are found mainly in the anal or genital areas in 5 to 22% of patients. The patches may less frequently develop in toe webs, oral commissures, face, inframammary folds and axilla. Patients may also experience hoarseness and sore throats because of inflammatory involvement of the tonsils, larynx and pharynx.
CNS involvement in the form of meningitis can also be seen in secondary syphilis. It usually occurs during the secondary rash and within the first 6 months of infection, in addition to cranial nerve involvement. Similarly, deafness and optic neuritis may also develop.