A 20-year-old female developed a lichenoid reaction on the side of her tongue after an orthodontic procedure!
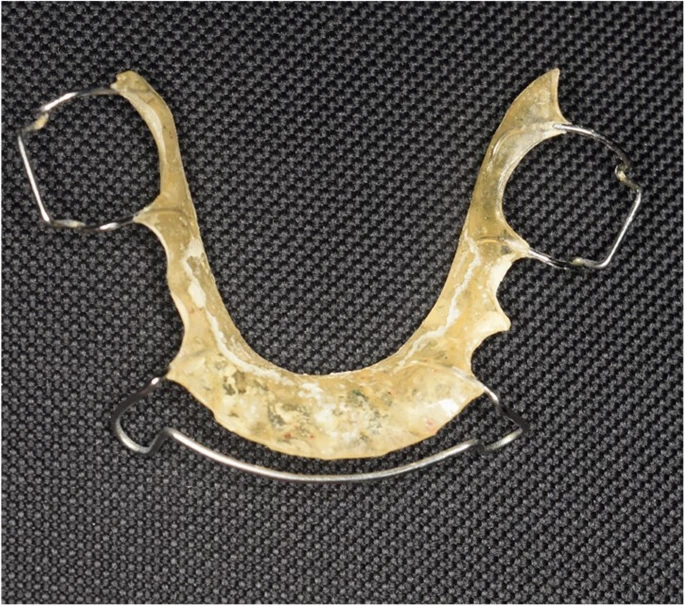
She presented to the clinic with a complaint of a painful lesion on her tongue. According to her, the lesion was one year old and had gradually increased in size. Moreover, she reported undergoing a dental procedure two years ago and using a Hawely retainer.
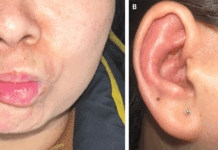
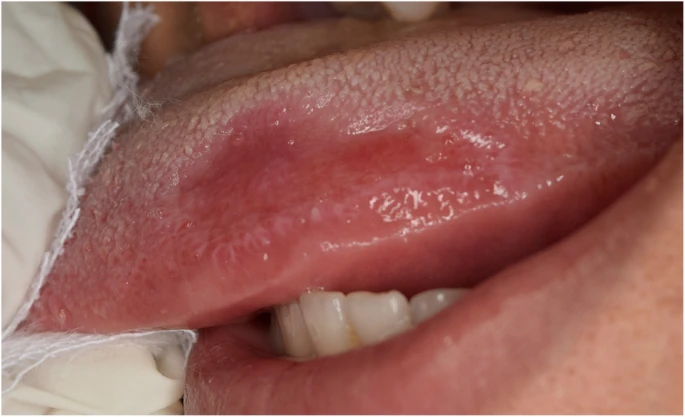
The patient did not have any significant medical history. Nor did extraoral examination reveal anything significant. However, on intraoral examination, doctors found a reddish lesion on the left lateral side of the tongue. They also noticed a white lesion on the right side of the tongue. The white lesion resembled leukoplakia as seen in oral thrush. Hence, doctors included lichenoid reaction in their differentials along with erythroplakia and geographical tongue.
Histopathology Reveals Lichenoid Reaction
Doctors did a biopsy of the affected area and sent it for histopathology. Results showed keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with interspersed areas of atrophy. Results also revealed lymphocytic infiltrate in the lamina propria evident of an inflammatory reaction. Based on these findings, doctors made a diagnosis of oral lichenoid reaction (OLR). To confirm their diagnosis, they proceeded with a patch test. They used the same material as that of the retainer and applied it to the patient’s forearm. Within 72 hours, the patient developed erythema and pigmentation indicative of a positive patch test.
Oral Lichenoid Reaction: What Do We Know?
Oral lichenoid reaction (OLR) refers to a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction in the oral mucosa to an inciting agent. It competes with oral lichen planus which presents with similar symptoms as OLR. Doctors differentiate between the two based on the history and the establishment of an inciting agent.
There can be various triggers for lichenoid reactions. It can set in as an immune response to materials used during orthodontic restoration procedures such as metal wires and drugs. It can also develop as an allergic reaction to different agents in toothpaste and food additives. Medicines used for the treatment of systemic disease such as SLE can also cause OLR. In any case, the presence of a trigger is mandatory (as in this case of the Hawley retainer).
Clinical and Histological Features
Clinically, OLR can manifest both in the form of extraoral and intraoral lesions. In both conditions, it can cause the development of bullae, erosions or erythematous lesions. Interestingly, almost all of its clinical features overlap with those of lichen planus and it becomes very difficult to distinguish between the two. Only histopathological analysis helps yield a definitive diagnosis.
On histology, the most striking feature of lichenoid reaction is the presence of lymphocytic infiltrates in the lamina propria that often extends into the epithelium as well. Moreover, the presence of cellular dysplasia also differentiates OLR from lichen planus.
Treatment of Oral Lichenoid Reaction
In our patient, the trigger for oral lichenoid reaction was the Hawely retainer. Hence, doctors advised the patient to remove the retainer. They instructed her to replace it with a vacuum retainer instead. With the offending agent not in place anymore, the lesion started to regress. In just 3 weeks, the lesion resolved dramatically. A follow-up after six months showed the absence of lesion altogether.
The Bottom Line
Oral lichenoid reaction subsumes dysplasia and thus carries a potential for malignancy. It should be quickly diagnosed based on history and histopathological findings. Moreover, the associated offending agent should be immediately removed. There have been many cases of OLR associated with certain resins and medication but OLR caused by a Hawely retainer is something very unusual.
Hawley retainers are popularly used for orthodontic retention. If caution is not practised and the patient is not assessed for any adverse effects, he can develop a lichenoid reaction over time. Thus when using such a retainer, one should test for allergic tendencies using a patch test. However, the patch should be of the same material as the retainer to yield a reliable result.