A 61-Year-Old Woman Presenting with Low Back Pain Diagnosed with IgG4-Related Disease
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) refers to a group of immune-mediated fibro-inflammatory conditions that affect multiple organs. Increased IgG4 serum levels support the diagnosis of IgG4-RD, as does the typical histopathology of fibrous infiltrates or masses containing IgG4-positive plasma cells. A 61-year-old woman with low back pain was diagnosed with IgG4-RD involving the thoracoabdominal aorta and retroperitoneum.
Case study: IgG4-related disease
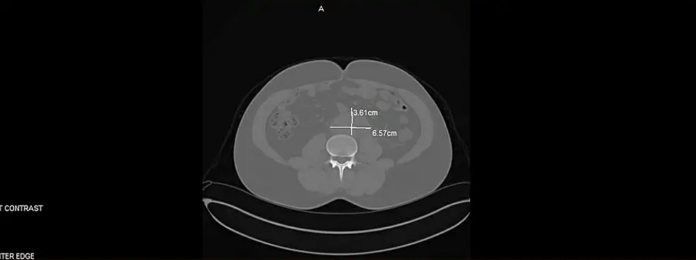
A 61-year-old woman with persistent low back pain was referred to a hospital in South Korea. The thoracoabdominal aorta, iliac vessels, and retroperitoneum were found to have diffuse circumferential infiltrates on computed tomography (CT) and 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/CT (F-18-FDG-PET/CT). The serum IgG4 level was 418.0 mg/L. (reference range: 30-2000). She had a laparoscopic retroperitoneal biopsy and a cystoscopic double-J ureteral stent placed. Histopathological examination revealed IgG4-positive plasma cells, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, and fibrosis. She was diagnosed with IgG4-RD and was treated for 6 months with glucocorticoids (GCs).
Due to an occlusion of the right iliac arteries, she underwent femoral-to-femoral bypass graft surgery for revascularization
She relapsed after discontinuing GC, and GC administration was resumed. She had difficulty tapering GC use due to persistent low back pain, which improved with combined GC and immunosuppressant treatment.
Based on the 2019 classification criteria, this article highlights the case of IgG4-RD involving the thoracoabdominal aorta and retroperitoneum. Similarly, radiological studies of IgG4-RD have grown in importance, and F-18-FDG-PET/CT, a functional imaging modality of the entire body, is a valuable evaluation method for diagnosis and clinical outcomes.
The results of the physical examination were unremarkable
The blood tests showed anaemia (9.2 g/dL haemoglobin [reference range: 12-16], 29.3% hematocrit\s[reference range: 36-46]) and increased inflammatory markers (21.34×103\s/μL white blood cells [WBC; reference range: 4.0-10.0×103\s] with 80% neutrophils [reference range: 40-80%],\s0.2% eosinophils [reference range: 1-7%], and 12.96 mg/dL\sCreactive protein [CRP; reference range: less than 0.3]). Despite consistently elevated WBC and CRP levels, the body temperature remained within normal limits, and no other signs of infection were observed. Serum IgG4 concentration was calculated to be 418.0 mg/L. (reference range: 30-2000).
The ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending aorta, bilateral common iliac artery bifurcation, right internal iliac artery, and retroperitoneum were all found to have diffuse circumferential infiltrative soft tissue lesions with contrast enhancement on chest and abdominopelvic CT. The right common iliac vein had deep vein thrombosis. In addition, multiple lymph nodes in the paraaortic and aortocaval areas were enlarged.
Despite the fact that the blood laboratory test results showed that the values were within the normal range of renal function, there was right obstructive hydronephrosis
A diuretic renal scan using Tc-99m MAG3 revealed a dilated renal pelvis with partial urinary obstruction for the right kidney and decreased renal function. Moreover, on F-18-FDG-PET/CT, there was also diffuse heterogeneous F-18-FDG uptake along the aortic arch (SUV max: 13.3) involving the origin of three branches without obstruction and the abdominal aorta from the gastroesophageal junction to both the common and right internal iliac arteries, with a prominent hypermetabolic lesion in the right common and internal iliac arteries (SUV max: 9.2).
Under general anaesthesia, the patient underwent a laparoscopic retroperitoneal biopsy of the fibrotic lesion around the infrarenal aorta and common iliac arteries, and a double-J ureteral stent was placed through cystoscopy. Histopathological and immunohistochemical staining revealed dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with 16 IgG4-positive cells per high-power field and a 13% ratio of IgG4-positive cells to IgG-positive cells. There was phlebitis with obliterative changes. There was marked diffuse fibrosis but no obvious storiform pattern.
Conclusions
In conclusion to the findings, the role of radiological studies in the diagnosis and treatment response evaluation of IgG4-RD with systemic multiorgan involvement is increasing. F-18-FDG-PET/CT, a whole-body functional imaging modality, is useful for disease activity monitoring, response evaluation, and drug development.
For revascularization of the arterial blood flow in the lower extremities, the patient underwent emoral-to-femoral bypass graft surgery. Whereas around one month after surgery, the low back pain and urinary frequency returned, and IgG4 (321 mg/L) and inflammatory markers (3.36 mg/dL CRP) level increased.
Treatment with an immunosuppressant (methotrexate; MTX 7.5 mg per week) added to the GC regimen of 15 mg/day improved the symptoms; it was then possible to gradually taper the GCs to 2.5 mg/day and high-dose GCs and immunosuppressants without a decrease in renal function or permanent complications.
Source: American Journal of Case Reports