Curtain sign and myasthenia gravis
The curtain sign (CS) is a sonographic artefact that is found in ultrasound studies. Generally, the artefact is used for describing the appearance of an expanded and aerated lung. The findings are often consistent with the diagnosis of pleural effusion. Curtain sign is a critical finding in emergency and critical care ultrasound for the early diagnosis of a pulmonary pathological process. The pathology diagnosed is often at the lateral lung-based and costophrenic recesses. This article describes the finding of curtain sign in a 23-year-old, diagnosed with myasthenia gravis.
Case study
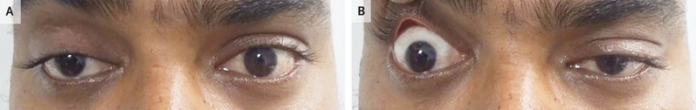
A 23-year-old patient presented to the neurology clinic with complaints of double-vision and right eyelid drooping with a history of 1 month. According to the patient, the eyelid drooping worsened at the end of the day. He also complained of slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and limb weakness. Doctors performed a neurological examination which showed restricted eye abduction and adduction on both sides with ptosis on the right side. Additionally, the manual raising of the ptotic eyelid caused drooping of the left eyelid. The findings are referred to as curtis sign or enhanced ptosis and are consistent with the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis. Further repetitive nerve stimulation of the patient’s patient’s orbicularis oculi muscle was significant for a decremental response. Similarly, acetylcholine receptor antibody levels were also elevated. Based on these findings, doctors diagnosed the patient with myasthenia gravis.
Doctors further advised a computed tomography of the chest which ruled out thymic abnormalities. Extraocular muscle involvement is often asymmetric and causes ptosis of the eyelid despite equal neuronal stimulation to the muscles on both sides. In the case of curtain sign, the passive elevation of the more ptotic eyelid decreases the neuronal stimulation on both sides. This causes the contralateral eyelid to relax. Treatment included pyridostigmine and prednisolone. The severity of the patient’s symptoms reduced significantly after a month.
Source: NEJM