Uric Acid Crystal Nephropathy secondary to erythodermic psoriasis.
This article presents the case of uric acid crystal nephropathy caused by erythodermic psoriasis. The disease is well described and has a rapid cell turnover, for example, tumour lysis syndrome. Therefore, it is important to recognise the rare complication early with administration of aggressive fluid resuscitation, urine alkalinization and uric acid lowering agents.
The 57-year-old male patient from Thailand presented with diffuse scaling of his skin.
He was diagnosed with long-standing psoriatic arthritis and was currently under treatment with adalimumab, leflunomide, and topical clobetasol. However, he stopped taking the medications two weeks before the presentation. The patient was a gardener by profession and was able to complete daily activities of living without any assistance. Although, during the disease course he suffered with diarrhoea which led to fatigue and diffuse scaling of the skin. He complained of chronic left ankle pain, also. However, he did not have any complaints of oral ulcers.
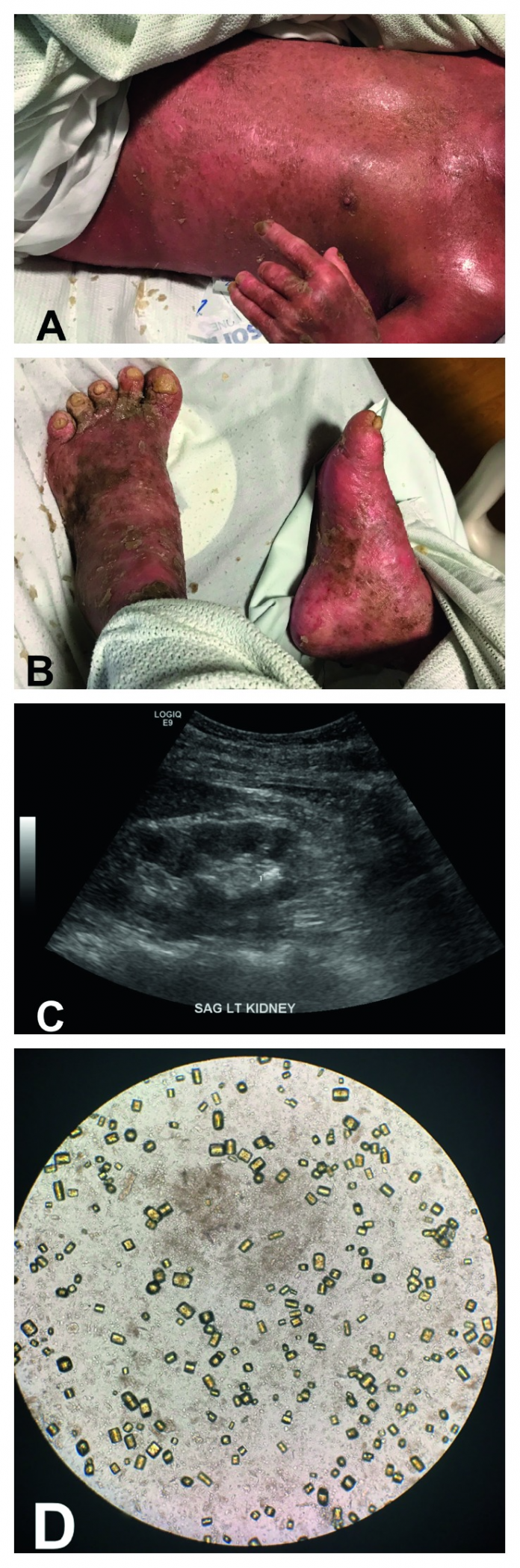
Physical examination was consistent with diffuse yellow scaling that covered his entire body.
Signs of underlying erythema and tenderness in the absence of mucosal involvement were also present. Doctors advised empiric antibiotics till an infection was ruled out. The patient had no prior history of renal disease. His test results showed high levels of creatinine consistent with acute renal failure. He was referred to the intensive care unit and administered 4 L of normal saline for initial resuscitation. However, the patient’s renal function did not improve despite the aggressive fluid administration. Over the next 48 hours the patient developed anuria, similarly, his creatinine and phosphate levels continued to peak.
Renal ultrasound showed a nonobstructing renal calculi in his left kidney, measuring 5 mm and small echogenic kidneys. The patient was diagnosed with uric acid crystal-induced nephropathy. Treatment included rasburicase, urinary alkalinization, and fluids. Leflunomide, topical isotretinoin, and clobetasol were restarted to treat the psoriasis. His renal function improved dramatically and he was discharged on topical clobetasol, leflunomide and secukinumab.
References
Erythrodermic Psoriasis Causing Uric Acid Crystal Nephropathy https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6458895/