Case Presentation: Gastrointestinal Tumors
A 79-year-old male presented to the emergency department with complaints of syncope and tachycardia. He also complained of fatigue, abdominal pain, and light-headedness for the last two months. He was a known case of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and atrial fibrillation.
Investigations
The doctors ordered some baseline laboratory tests including a complete blood count. The report revealed a low hemoglobin of 4.9 g/dl. Therefore, the doctors ordered blood transfusion of three packed red blood cells.
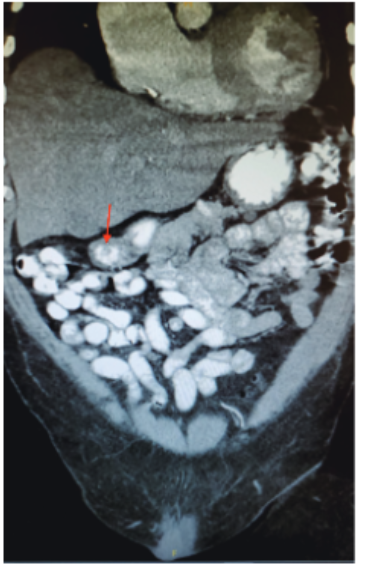
Based on this laboratory finding and the patient’s presenting symptoms along with medical history; the doctors ordered a CT abdomen and pelvis with contrast. ماكينات القمار The report of the CT scan confirmed the doctors’ suspicion of abdominal mass. The report demonstrated a duodenal tumor and a tumor in the pancreatic tail. Moreover, they also performed esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), for biopsy. This report confirmed the presence of a gastric adenocarcinoma grade III.
Treatment
After the confirmation of the diagnosis, the doctors performed an explorative laparoscopy for the resection of the found tumors. They removed the pancreatic tumor successfully. However, on removal of the gastric adenocarcinoma in the duodenum, they found another tumor in the posterior wall of the stomach, near the fundus. Thus, they sent the samples for all three tumors for biopsy to the lab. The biopsy results showed that the gastric adenocarcinoma had infiltrated into the submucosa and the pancreatic tumor was neuroendocrine in origin. Additionally, the tumor that the surgeons had found incidentally, was diagnosed as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (also known as GIST). Since the doctors discovered all the tumors at a stage where complete excision was possible, they did not advise chemotherapy post-operatively.
Recovery
After the surgery, the doctors evaluated the patient’s baseline investigations. His hemoglobin was 10.2 g/dl, 8.9 g/dl and 9.1 g/dl on day 1, 7 and 14 after the surgery, respectively. Furthermore, he did not complain of any syncope, abdominal pain or tachycardia.
Despite being rare cancers, gastrointestinal tumors have been on the rise for the past few years. They include cancers such as colo-rectal cancers, gastric cancers, pancreatic cancers, and liver cancers. Amongst these, GIST, anal cancers and neuroendocrine tumors are the rarest ones. The signs and symptoms are non-specific, such as anemia, weight loss and abdominal pain. Although in advanced cases they can present with organ-specific symptoms.
Doctors may find these tumors incidentally on imaging such as CT, MRI or ultrasound. Although, they make a definitive diagnosis based on the biopsy results. مواقع الرهان على المباريات
The management depends upon the stage at diagnosis, and can range from surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or even palliative treatment.
There are numerous risk factors that may predispose an individual to these tumors, which include cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, diets high in saturated fats and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Gastrointestinal tumors
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are mesenchymal tumors that are formed due to a mutation in tyrosine kinase genes, which causes malignant growth of interstitial cells of Cajal. These tumors also present with non-specific symptoms and are often found incidentally. Doctors can manage them efficiently with imatinib, which is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Imatinib has improved the management and prognosis of gastrointestinal tumors. Other management options include surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Gastric adenocarcinomas
Gastric adenocarcinomas are the most aggressive gastrointestinal cancers, accounting for 1% of all gastrointestinal cancers. They present with non-specific signs and symptoms, often making diagnosis difficult. Prognosis is worse if the patient is old, with lymph node metastasis or high-grade tumor.
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine tumors
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors originate from neural crest cells, and are classified into functioning and non-functioning tumors. The former consist of insulinoma, glucagonoma, gastrinoma and VIPoma. Whereas, the latter spread via tissue invasion. استراتيجية بينجو The management is similar to GISTs and gastric adenocarcinomas, consisting of surgical removal, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Additionally, doctors use medical management to treat symptoms associated with the release of hormones.
Prospect of Gastrointestinal Tumors
Gastrointestinal tumors are rare tumors that are found incidentally by doctors, during workup for other diseases. This case represents a unique case, where the doctors found 3 tumors simultaneously. The possible reason, for their quick diagnosis and therefore prompt treatment, which lead to avoidance of adverse complications; was due to the presence of GIST and the pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, with the gastric adenocarcinoma. If, there was a solitary gastro adenocarcinoma, doctors would not have been able to diagnose the condition early due to advanced disease at presentation. This is because solitary gastric adenocarcinomas, have non-specific symptoms and mimic peptic ulcers.
The unique nature and presentation of the patient in this case, warrants the need for keeping gastric carcinomas as a differential diagnosis when performing a work-up for non-specific signs and symptoms in the elderly.