Successful delayed reconstruction of biceps muscle
This article describes the case of a successful elbow flexion reconstruction in a 30-year-old male patient with compartment syndrome. The patient got into a road traffic accident and impact trauma to his left arm caused compartment syndrome.
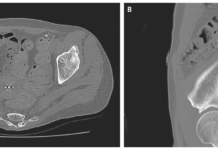
Surgical evaluation was significant for proximal biceps tendons rupture. Therefore, doctors suggested immediate repair and therapeutic fasciotomy. However, because of an unsuccessful repair, there was total necrosis of the biceps muscle. This led to the need of debridement of the biceps muscle. Literature reports several surgical procedures for the restoration of biceps muscle and simultaneously elbow flexion. The procedure is selected based on the requirements for each patient, including comorbidities, neurovascular injury and hand dominance.
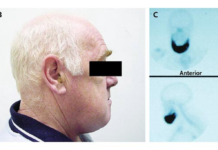
Doctors managed a successful delayed reconstruction of the muscle with an LD flap after stabilising the patient’s condition. As mentioned in the study, “the flap was harvested as free-pedicled, then modified into a tube-like shape to resemble the biceps muscle”.
Traumatic damage to the anterior compartment of the arm indicated the transfer of latissimus dorsi for restoring the elbow flexion
Although pedicled latissimus dorsi (LD) flap is rarely used for reconstructing biceps brachii soft tissue defects and restoring complete flexion. In this case, the 30-year-old underwent successful elbow flexion reconstruction using latissimus dorsi muscle.
This case report shows that transfer of latissimus dorsi muscle via a surgical procedure can successfully restore elbow function following upper limb trauma. The study states, “Traumatic damage to the anterior compartment of the arm is an indication for latissimus dorsi transfer, which can restore elbow flexion. Bipolar pedicled latissimus dorsi (LD) flap is a design used very rarely to simultaneously reconstruct biceps brachii soft-tissue defects and regain complete flexion function.”
This report shows that surgical procedure of transferring a latismus dorsi muscle can successfully restore elbow function following trauma. However, preoperative and postoperative planning are essential for functional reconstruction. Other essential factors that should be considered include degree of injury and optimal function restoration with minimal complications.
Source: American Journal of Case Reports