Giant stomach in a seventeen-month-old baby secondary to a congenital malformation
and ingestion of a Chinese strawberry.
A 17-month-old boy was brought
with complaints of vomiting and abdominal pain for the past 7 days. The child
had a history of congenital malformation of the gastric outlet. The boy was
given prokinetic agents considering the working diagnosis of functional
dyspepsia, which alleviated his vomiting.
Although his vomiting had stopped,
he was not asymptomatic. The boy was noticed to have continuous abdominal
distension leading to a giant stomach along with worsening of his mental status.
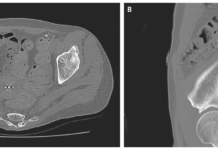
On a plain radiograph of the abdomen, a lot of gas was seen (Figure
1). A computed tomography scan was done, which revealed a significantly distended
stomach and 10 high-intensity shadows. CT scan also revealed a round focus of 1
cm in diameter, which was found obstructing the gastric outlet (Figure 2).
An intrathoracic gastric volvulus was identified on the
upper gastrointestinal imaging along with a wandering spleen, which together
impaired the transit of the intraluminal contents if the cardia.
On account
of the imaging results, the patient was diagnosed with gastric outlet
obstruction.
Gastrointestinal decompression was performed. Approximately 2000
ml of slightly red-colored gastric content was drained. The patient was
also provided with supportive care. Ultimately, the boy excreted the Myrica Rubra
kernels.
His symptoms had begun after eating the Chinese bayberry,
also called Chinese strawberry or Myrica Rubra. Ingestion of Myrcia Rubra,
coupled with the congenital malformation, made the condition even worse. The obstructed
stomach due to congenital malformation provided a harbor to the yeast to
reproduce and ferment the food.

Patients with gastric obstruction may present with nausea, postprandial and non-bilious vomiting, early satiety, abdominal pain, and weight loss in chronic cases. The obstruction may be mechanical or due to motility disorders. لعبة سلوتس In the latter, a majority of the cases remain unrecognized; the recognized medical conditions include diabetes mellitus, viral infections, and certain medications, including anticholinergics and opioids. لعب قمار The mechanical causes include:
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs. - Polyps
- Gastric volvulus
- Gastric tuberculosis
- Strictures
- Helicobacter pylori (H.
pylori) - Gastric carcinoma
- Gastric lymphoma
There are high chances of misdiagnosis of gastric obstruction in patients with congenital malformation; therefore, it has a poor clinical outcome. It is imperative to diagnose promptly and accurately, and manage earlier in the course to improve the poor clinical outcome. betfinal
References:
Kumar A, Annamaraju P. Gastric Outlet Obstruction. [Updated 2020 Jun 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557826/
Yu Y, Shi Y, Li Q, Zhang Y (2018) A Case of Gastric Obstruction: A Giant Stomach. Clin Med Img Lib 4:121. doi.org/10.23937/2474-3682/1510121