Olanzapine-induced acute angle closure glaucoma
An uncommon ocular emergency called olanzapine-induced acute angle closure glaucoma (DICAG) may develop after the administration of some topical and systemic drugs. Patients with AAC first experience abrupt, severe ocular pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, blurred vision, and seeing haloes around lights. A history of AACG in the opposite eye, Asian ethnicity, family history, female sex, hyperopia, narrow angles, short axial length, and advanced age are all known risk factors for AACG. Acute angle closure (AAC) attacks happen when there is a blockage in the passage of aqueous outflow to the trabecular meshwork. This can happen when the pupil dilates due to factors such as low light, emotions, or negative drug side effects.
An uncommon ocular emergency called drug-induced acute angle closure glaucoma (DICAG) may develop after the administration of some topical and systemic drugs
Patients with AAC first experience abrupt, severe ocular pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, blurred vision, and seeing haloes around lights. A history of AACG in the opposite eye, Asian ethnicity, family history, female sex, hyperopia, narrow angles, short axial length, and advanced age are all known risk factors for AACG. Acute angle closure (AAC) attacks happen when there is a blockage in the passage of aqueous outflow to the trabecular meshwork. This can happen when the pupil dilates due to factors such as low light, emotions, or negative drug side effects.
Diagnosis and treatment
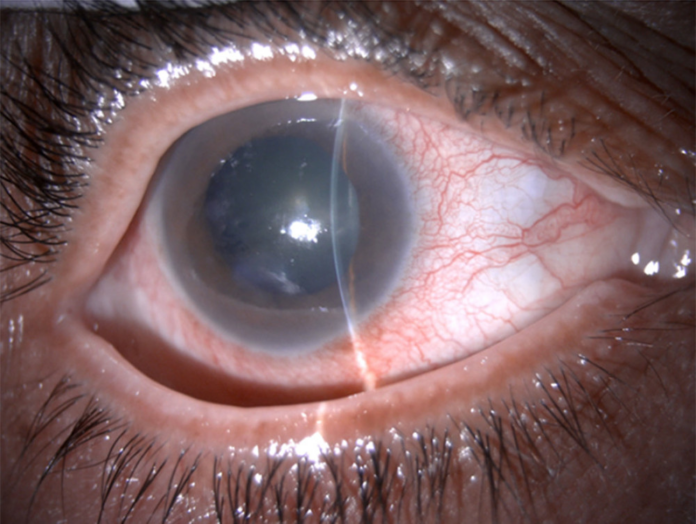
The examination of the other eye revealed nothing notable. A gonioscopic examination revealed a narrow-angle in the left eye and an appositionally closed angle in the right eye. Using ultrasound biomicroscopy, a shallow AC with 360-degree angle closure was identified. Timolol maleate 0.5% and brimonidine tartrate 0.15%, two topical IOP-lowering medications, as well as oral systemic acetazolamide, were administered to the patient. After using pilocarpine 2% to contract the pupil, the right eye underwent a therapeutic Nd: YAG laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI), and the left eye underwent a preventative LPI.
The patient’s symptoms and physical signs greatly improved the next day. The drug-induced pupillary lock was diagnosed when pupillary block appeared quickly after taking a medication having anti-cholinergic effects, such as olanzapine.
Source: American Journal of Case Reports