Patient diagnosed with multiple myeloma dies of Bortezomib induced pulmonary toxicity.
This article describes the case of a 64-year-old male patient with lower back pain who presented to the emergency department with acute, severe mid back pain radiating to bilateral shoulders. He was diagnosed with multiple myeloma for which he was given CyBord radiotherapy and developed pulmonary toxicity induced by Bortezomib.
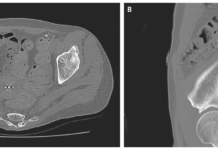
Doctors advised a CT scan to rule out aortic dissection. The CT scan showed multiple lytic lesions in the bony skeleton with a compression fracture at T7 vertebral body and soft tissue epidural extension. The CT findings were further confirmed with a bone survey. In addition, bone marrow biopsy was consistent with the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. For which the patient was advised advised radiation therapy to the thoracic spine. Similarly, he completed 2 cycles of CyBorD, Bortezomib and dexamethasone regimen by mouth.
3 days after the second cycle was completed, the patient presented back to the hospital with respiratory distress.
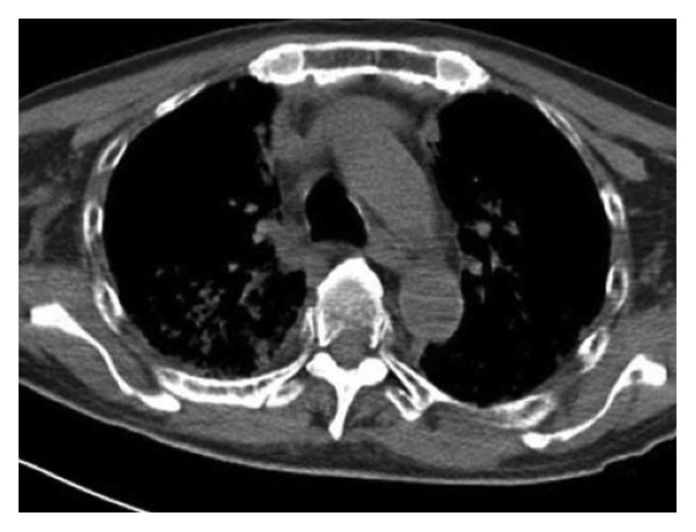
Repeat CT chest was significant for new interval appearance of bilateral perihilar ground-glass opacities. Similarly, interstitial thickenings which were not seen in the previous scans were also predominant in the upper lobes. He did not show any other signs or symptoms of cough, fever or leukocytosis. Doctors discharged the patient after he showed improvement with oral prednisone. However, he had to be readmitted because of worsening respiratory distress after 4 days.
CT chest was repeated which showed improvements in the previously defined perihilar ground-glass opacities. Although, hazy areas of ground-glass opacities were evident in the bilateral lower lobes of both lungs. He was given high-dose methylprednisone and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation. But, he showed no improvement and died on the 10th day of admission.
References
Bortezomib-Induced Pulmonary Toxicity: A Case Report and Review of Literature https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6286773/