Tuberculous flexor tenosynovitis presenting with swelling over the wrist and palm
Tuberculous flexor tenosynovitis of the hand has very few reported cases in literature. The condition is also referred to as compound palmar ganglion and represents a total of 5% of bone and joint tuberculous infections. The ulnar and radial bursae of the hand are two of the most commonly affected sites. In addition, these bursae are interconnected in at least 80% of the population and give rise to horseshoe-shaped tenosynovitis. This article describes the case of a 50-year-old man who presented with a complaint of swelling over his left wrist and palm. The patient was a butcher by profession and worked at a fish market.
The patient’s swelling was initially small and painless without any signs of trauma, weight loss, fever, cough or night sweats. He also had no previous contact with anyone with tuberculosis. According to the patient, the size of the swelling increased over the last 4 years further involving the wrist, hypothenar eminence and the distal interphalangeal joint. Symptoms included mild pain and discomfort restricted to the distal interphalangeal joint. He also complained of a tingling sensation and paraesthesia over the region of the median nerve and the pain aggravated during the night.
Examination findings and treatment approach
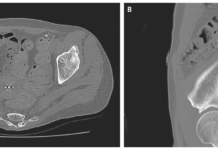
Examination showed that the swelling was soft, doughy, strong and cross-fluctuant. Gritty crepitus was also evident on palpation. Doctors advised an X-ray of the wrist, hand and chest which showed local soft tissue deformity. بينجو اون لاين There were no other bone deformities noted. Other findings included a scar over the ulnar aspect of the palm. Before presenting to the clinic, the patient underwent a needle aspiration somewhere else. كازينو 888 The culture fluid did not show any signs of bacterial infection. Doctors further advised an MRI of the hand which was significant for thickened synovium with internal T2 hypointense foci surrounding the flexor tendon. The hematological reports were also within normal range. Mantoux test results came back negative.
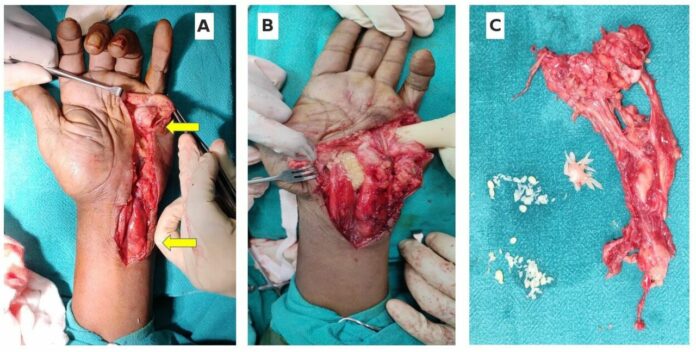
After all investigations, doctors further advised an excisional biopsy for the tenosynovium. During the biopsy, a gross swollen tenosynovium was found at the ulnar region of the wrist and hypothenar region. العب وربح Intraoperative findings were consistent with compound palmar ganglion. After thoroughly washing the wound, it was closed in layers. Histopathology confirmed the presence of tuberculosis. The patient was started on anti-tubercular therapy. There were no signs of recurrence of swelling at 6-month follow-up and movements of the wrist and finger were also normal.
References
Patient with tuberculous flexor tenosynovitis of the hand https://casereports.bmj.com/content/14/5/e243091