Severe aplastic anemia complicated by a deadly fungal infection ultimately leading to death.
A 72-year-old male, who was referred for consultation as his blood reports indicated pancytopenia, later succumbed to death due to a fungal infection. At the initial presentation his complete blood count showed the following values:
- Hemoglobin – 6.4 g/dL
- White blood cell (WBC) – 2.1 × 109/L
- Neutrophil count 0.4 × 109/L.
- Platelets – 7 × 109/L.
- Absolute reticulocyte count – 1.79 × 109/L.
Due to anemia, lymphopenia, and thrombocytopenia, he received packed red blood cells and platelet concentrates once or twice a week.
A bone marrow study revealed increased fat content and severe hypoplastic marrow. Chromosomal analysis showed a normal karyotype.
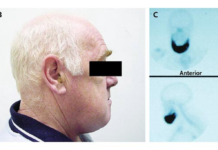
The patient had a history of lumbar fusion surgery; therefore, magnetic resonance imaging was not suitable for this patient. However, bone marrow scintigraphy was performed using Indium Chloride, which showed no bone marrow activity in any of the bones except for mild bone marrow activity in vertebrae.
The patient was diagnosed with Severe Aplastic Anemia (SAA). العاب بوكر اون لاين
Start of Fungal infection:
Subsequently, the patient developed bacterial pneumonia, which responded to cefepime. After that, the doctors started him on immunosuppressive therapy (IST) consisting of Rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (rATG), cyclosporine, and steroids.
For prophylaxis against fungal infection, they added 50 mg/day of micafungin.
Progression of disease:
Despite the immunosuppressive therapy (IST) and the administration of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, the neutrophil count remained below 0.2 × 109/L. Twenty days after starting IST, the patient developed a low-grade fever. He was found to be suffering from Enterococcus faecium bacteremia, so vancomycin was added to cefepime.
The patient’s condition deteriorated despite adequate antibiotic therapy, and he started having a high-grade fever. The follow-up blood cultures were negative for bacteria or fungi.
Cefepime was stopped; instead, the patient was given doripenem. The dose of micafungin was also increased.
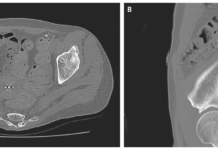
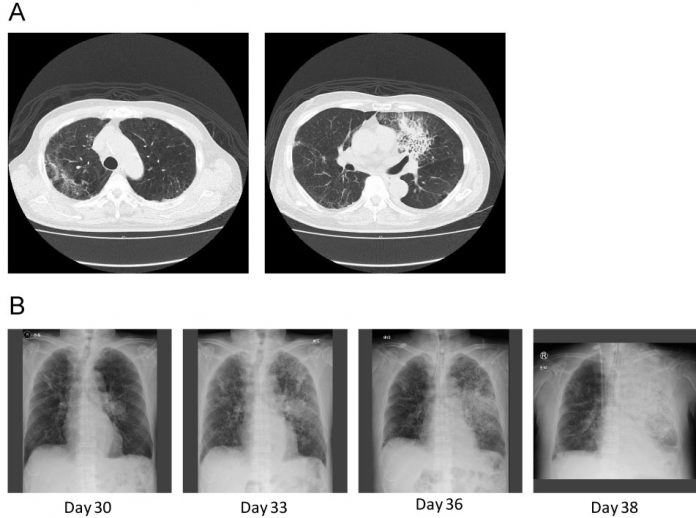
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest revealed a new consolidation in the left lung’s upper lobe (along with the old changes from the consolidation in the upper lobe of the right lung). There were no cavitations or any other typical findings of fungal infection on the chest CT.
Multiple sputum cultures grew no organism.
The patient deteriorated enough to warrant mechanical ventilatory support. The patient didn’t fulfill the clinical criteria nor had the laboratory proof of fungal infection. لعبة فلوس حقيقية The patient’s pneumonia worsened despite broad-spectrum antibiotics.
The patient didn’t show any improvement until micafungin was replaced with caspofungin on day 31.
The patient’s condition deteriorated, and he developed severe disseminated coagulopathy and suffered a multi-organ failure. لربح المال He eventually succumbed to death on the 36th day.
On the day of his death, sputum culture revealed zygomycetes.
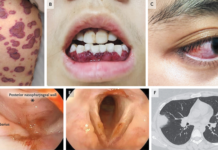
An autopsy revealed massive necrosis and thrombosis in multiple organs. The thrombotic vessels contained fungus. Culture of a sample from the left lung grew Rhizomucor.

A) Gross image of bilateral lungs;
B) Hemorrhagic infarction and pulmonary artery thrombosis of the left lung;
C) Histologic finding of pulmonary artery embolization caused by mucor hyphae;
D) Fungal embolization causing renal infarction;
E) Myocardial hemorrhagic infarction;
F) Mucor hyphae
References:
Tashiro H, Oshima Y, Sumiyoshi R, Matsuo T, Yamamoto T, et al. (2019) Fatal Systemic Mucormycosis after Rabbit Anti-Thymocyte Globulin Therapy in a Severe Aplastic Anemia Patient. Int J Blood Res Disord 6:039. doi.org/10.23937/2469-5696/1410039